
Do you want to talk more about choosing the right financial solutions for your business? Take a look at Vena’s financial reporting solutions here, or reach out to discuss what’s right for you. Most larger companies choose the indirect method, at least in part because of the lower time investment, while analysts often prefer it as well because it lets them see for themselves what adjustments assets = liabilities + equity have been made. Alternatively, the direct method begins with the cash amounts received and paid out by your business.
Direct vs. Indirect Method of Cash Flow Presentation

Make sure your accounting practices align with GAAP to enhance reliability and transparency. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment https://www.wearetechinnovator.com/blog/enron-scandal-and-accounting-fraud-what-happened/ analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. The non-cash expenses and losses must be added back in and the gains must be subtracted. During the year, depreciation expense and amortization expense amounted to $20 million and $3 million. Taxes paid, interest paid, and dividend paid amounted to $25 million, $8 million and $15 million.
More Accurate
- Instead of directly reporting cash inflows and outflows, this method reconciles the differences between net income and net cash provided by operating activities.
- This offers a clear, straightforward look at where money is coming in and going out.
- Other non-cash items include impairment charges, which reduce an asset’s book value, or stock-based compensation expense, where employees receive stock instead of cash.
- Plus, if a business is a publicly traded company, they will be required to report an indirect method cash flow statement under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) requirements.
- However, the more you grow and scale your business, the less feasible it may be to utilize the direct method.
- My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers.
A cash flow statement is a core financial report that tracks the inflows and outflows of cash within a business over a specific period. The cash flow statement specifically records cash inflows and outflows, helping to clarify the sources and uses of cash during the reporting period. Both the direct and indirect methods have their place in managerial accounting, and understanding their differences is crucial for effective financial analysis and decision-making. By mastering these methods, you will be better equipped to analyze cash flows, make informed decisions, and succeed in your accounting exams.
- During reconciliation, it is important to ensure that cash balances align with the figures reported in your cash flow statements for accurate liquidity reporting.
- Plus, most major accounting software packages are optimized for this method, further streamlining month-end close and reporting.
- Accrual accounting is the backbone of modern financial management, as it provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial performance.
- A negative cash flow statement can be a strong indicator that your company’s not in a good position for a potential economic downturn or market shift.
- Understanding these methods will help you analyze financial statements, make informed financial decisions, and evaluate a company’s financial performance and liquidity position.
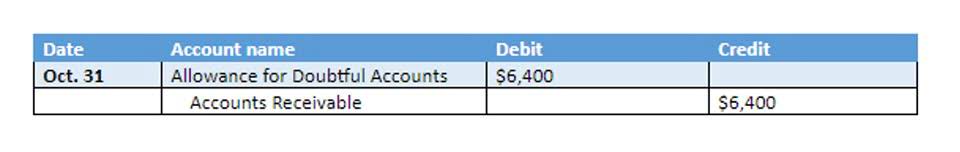
- An Accounts Receivable increase means sales were recognized as revenue, but cash has not been collected.
Example 1: Direct Method Cash Flow Statement
It might be helpful to look at an example of what the indirect method actually looks like. Cash Flows from operating Activities are primarily derived from the Principal Revenue-producing activities of the enterprise. Cash Flow Statement also known as Statement of Cash Flows is a statement which shows the Changes in the Cash Position of an organisation between 2 periods. Along with showing the changes in the Cash Position of an organisation, it also cash from operating activities differs between the direct and indirect method with respect to the: depicts the reasons for such change during the period. Additionally, the regulations your business is subject to could determine which method you will need to utilize. Smaller organizations with a limited number of transactions each month can likely manage the level of tracking and detail that the direct method requires for accuracy.

Direct method accounting can be especially useful for business owners seeking granular detail, though it may require more effort to compile the necessary data. The direct cash flow statement serves as a key reporting tool, utilizing the direct cash flow method to present these details. To calculate cash flow using the direct method, list all cash receipts and cash payments to determine the net cash position for the period. In conclusion, the direct method and the indirect method are two different approaches to preparing the cash flows from operating activities section of the statement of cash flows. While the direct method provides more detailed information, it is more time-consuming and costly to prepare.

Importance in Financial Analysis
Understanding these methods will help you analyze financial statements, make informed financial decisions, and evaluate a company’s financial performance and liquidity position. The choice between the direct and indirect cash flow methods depends on several factors, including reporting requirements, available resources, and the desired level of granularity. While the direct method provides a more detailed view of cash flows, the indirect method reconciles net income to net cash provided by operating activities. Choosing between the direct and indirect methods depends on your business’s size, reporting requirements, and the depth of cash flow analysis desired. The direct method gives greater cash insight but is more labor-intensive, while the indirect method fits seamlessly with standard accounting practices and is widely accepted by lenders and investors.
What is the Direct Method for Cash Flow Statements?
- To calculate cash flow using the direct method, list all cash receipts and cash payments to determine the net cash position for the period.
- This is in comparison to the tedious nature of the direct method, where preparers need to monitor and document each cash inflow and outflow for the business.
- The direct cash flow method of cash flow reporting provides a transparent look at direct cash flow transactions from operations.
- The company paid $150,000 in cash to suppliers for inventory, $75,000 in cash to employees, $25,000 in cash for rent and utilities, and $10,000 in cash for taxes.
- This method is more commonly used due to its simplicity and alignment with accrual accounting.
- In Canada, companies must adhere to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE), depending on their classification.
- An increase in a current asset (excluding cash), like Accounts Receivable or Inventory, generally means cash was not received or was used.
Classification by activities provides information that allows users to assess the impact of those activities on the financial position of the enterprise. This information also helps in evaluating the inter-relationships between these activities. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them often depends on the company’s preferences and regulatory requirements. The direct method requires detailed tracking of every cash transaction, which can be labor-intensive. As we mentioned above, the indirect method is the required/preferred method under GAAP and IFRS accounting regulations. This is in comparison to the tedious nature of the direct method, where preparers need to monitor and document each cash inflow and outflow for the business.
